The Role of Identity in Effective Leadership
Learn to understand and balance your various identities at work, leading to enhanced decision-making, team dynamics, and overall leadership effectiveness using these practical strategies and exercises.
Section 1: What Are The Core Identities of a Leader?
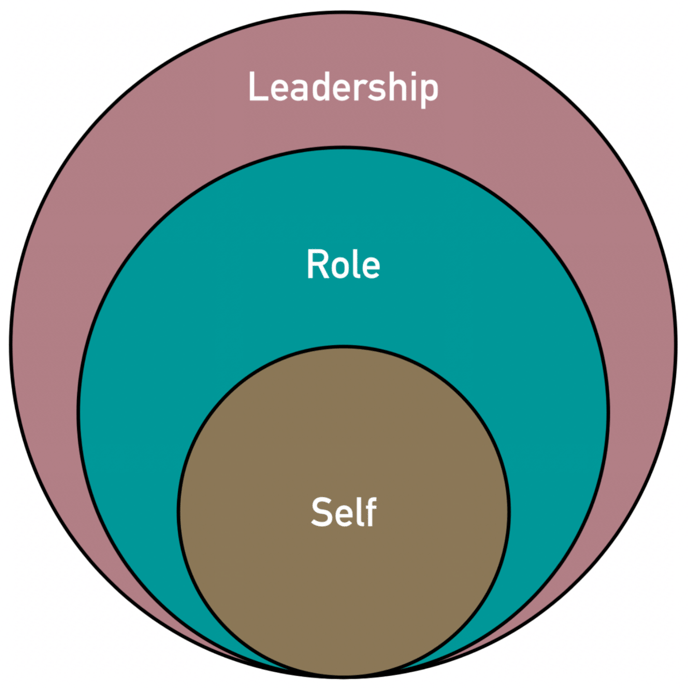
All identities are characterized by two key characteristics; a) differentiation - it's how you "know you are you", and b) continuity - it's how you "know you are still you" despite growth and change.
When it comes to being a leader, there are three core identities that will come into play as you navigate your day:
1) Self-Identity: this is who you are when acting through your core personality traits and values, and how they shape your perceptions and how you prefer to communicate. The bulk of these are described by your Cognitive Colour.
2) Role Identity: this is who you are when carrying out specific functions and responsibilities within the organization that guide the tasks and objectives of yourself and others.
3) Leadership Identity: this is who you are in situations where you hold power over others and must balance your influence with empathy and fairness - increasing the importance of those around you.
Section 2: Anatomy of An Identity
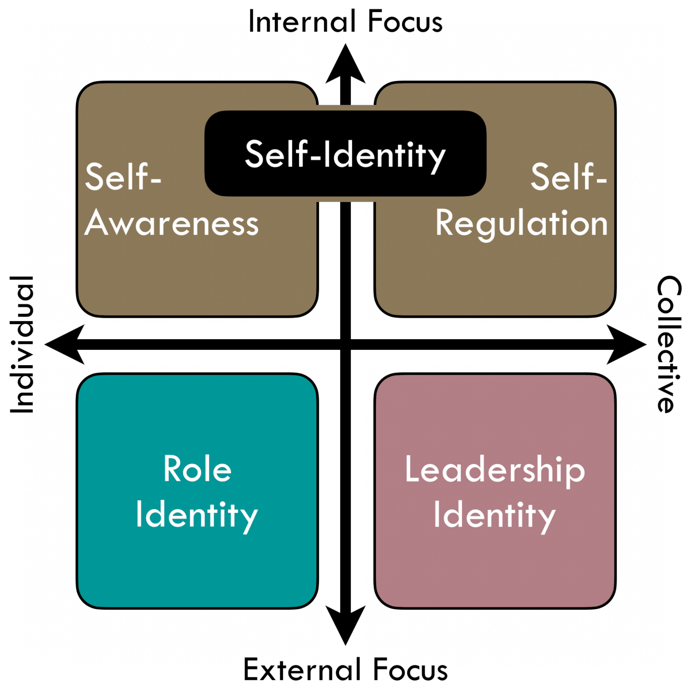
Our identities are a product of our Internal self-reflective focus on how our environment shapes us vs our External focus on how we shape our environment.
Both result in a system of feedback that sees us test our identity and gauge the reaction we get. Over time enough loops that reward certain behaviour and help us avoid consequences - all “cement” together to form an identity - offering the consistency and differentiation that are the function of identity.
Your Self-Identity formed when your enduring strengths and weaknesses led to reward and consequence across a wide variety of situations. This is why it is treated within the framework as you core identity.
Your Role Identity formed based on your choices and behaviours and the degree to which they led to you meeting, exceeding or falling short of the expectations of your job function.
You Leadership Identity formed as you began to exercise power and influence and you saw the changes in others’ behaviour that resulted.
Section 3: How Identity Applies to Lessons in This Training:
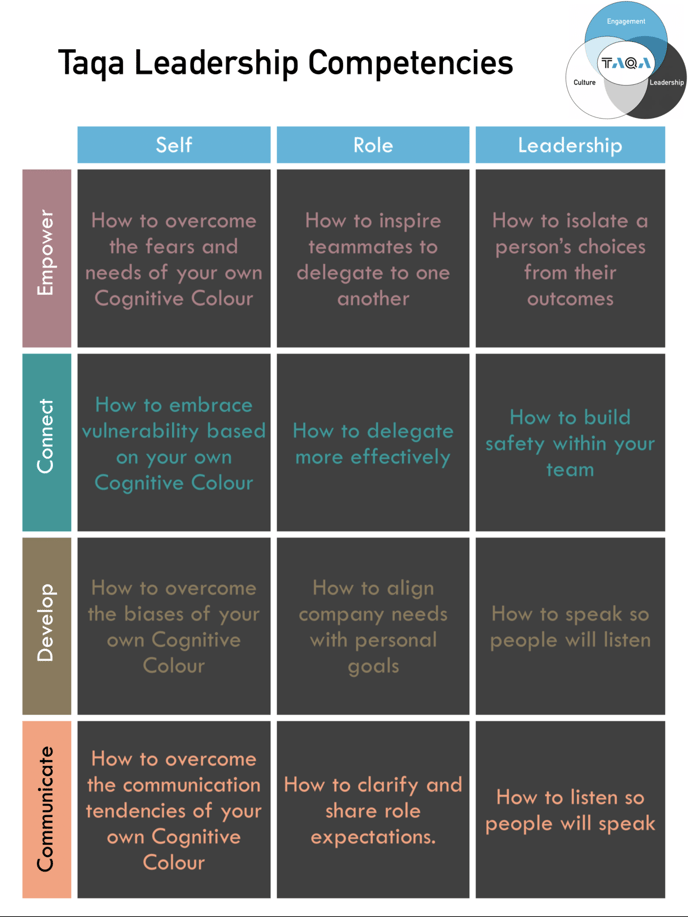
The 12 lessons in this training are listed above - segmented by your 4 Leadership Commitments as well as the 3 Identities. Each week we will focus on one of the Leadership Commitments, from Empower to Connect to Develop to Communicate.
It is beneficial to understand the specific role Identity plays in each:
Lessons Involving Self-Identity:
Lesson #1: How to Overcome the Fears and Needs of Your Own Cognitive Colour:
Why This Requires Self-Identity: Understanding and overcoming fears and needs specific to your Cognitive Colour requires deep self-awareness. Operating from your true self helps you address these personal challenges effectively.
- Challenges of Operating from Role Identity: Role identity focuses on job responsibilities, potentially neglecting personal fears and needs. This can lead to stress and decreased job satisfaction.
- Challenges of Operating from Leadership Identity: Leadership identity emphasizes authority and influence. This may cause leaders to overlook their own vulnerabilities, leading to ineffective self-management.
Lesson #4: How to Embrace Vulnerability Based on Your Own Cognitive Colour:
Why This Requires Self-Identity: Embracing vulnerability is a deeply personal process. It helps build trust and authenticity, crucial for self-growth.
- Challenges of Operating from Role Identity: Role identity may push you to hide vulnerabilities to meet professional expectations, reducing genuine connections.
- Challenges of Operating from Leadership Identity: Leadership identity may prioritize strength over vulnerability, making it difficult to build trust and authenticity with your team.
Lesson #7: How to Overcome the Biases of Your Own Cognitive Colour:
Why This Requires Self-Identity: Identifying and overcoming biases requires introspection and self-awareness. It ensures personal growth and unbiased decision-making.
- Challenges of Operating from Role Identity: Role identity may reinforce biases, as professional roles can come with predefined judgments and expectations.
- Challenges of Operating from Leadership Identity: Leadership identity may amplify biases, affecting fair decision-making and undermining trust within the team.
Lesson # 10: How to Overcome the Communication Tendencies of Your Own Cognitive Colour:
Why This Requires Self-Identity: Improving communication tendencies requires self-awareness of personal styles and adapting them to be more effective.
- Challenges of Operating from Role Identity: Role identity may constrain communication to job-related norms, limiting personal expression and clarity.
- Challenges of Operating from Leadership Identity: Leadership identity might impose a communication style that doesn't resonate with personal authenticity, reducing effectiveness
Lesson Involving Role Identity:
Lesson # 2: How to Inspire Teammates to Delegate to One Another
Why This Requires Role-Identity: Encouraging delegation among teammates involves understanding team roles and dynamics. Operating from your role identity helps align team efforts with organizational goals.
- Challenges of Operating from Self-Identity: Focusing on personal traits can lead to biased encouragement, ignoring team dynamics and organizational needs.
- Challenges of Operating from Leadership Identity: Prioritizing authority might cause over-reliance on leadership for delegation, stifling team initiative and autonomy.
Lesson #5: How to Delegate More Effectively:
Why This Requires Role-Identity: Effective delegation requires a clear understanding of team roles and individual strengths. Role identity ensures tasks are assigned appropriately to achieve goals.
- Challenges of Operating from Self-Identity: Personal preferences may lead to biased delegation, ignoring team capabilities and project needs.
- Challenges of Operating from Leadership Identity: Emphasizing authority can lead to micromanagement, undermining team trust and autonomy.
Lesson # 8: How to Align Company Needs with Personal Goals
Why This Requires Role-Identity: Aligning company needs with personal goals requires understanding both organizational objectives and individual roles. Role identity bridges these for mutual benefit.
- Challenges of Operating from Self-Identity: Personal goals might overshadow organizational needs, causing misalignment and reduced productivity.
- Challenges of Operating from Leadership Identity: Focusing solely on organizational goals can neglect individual aspirations, reducing motivation and engagement.
Lesson #11: How to Clarify and Share Role Expectations:
Why This Requires Role-Identity: Clarifying and sharing role expectations involves understanding job functions and responsibilities. Role identity ensures clear communication and alignment within the team.
- Challenges of Operating from Self-Identity: Personal biases might cloud role expectations, causing confusion and miscommunication.
- Challenges of Operating from Leadership Identity: Emphasizing leadership perspectives can overshadow specific role details, leading to unclear expectations and inefficiencies
Lessons Involving Leadership Identity:
Lesson #3: How to Isolate a Person’s Choices from Their Outcomes:
Why This Requires Leadership-Identity: Separating choices from outcomes requires understanding broader team dynamics and avoiding blame. Leaders must create a culture of learning and growth.
- Challenges of Operating from Self-Identity: Personal biases can lead to unfair judgments, reducing trust and morale within the team.
- Challenges of Operating from Role Identity: Focusing on job tasks may ignore the need for holistic understanding, leading to blame and fear of failure.
Lesson #6: How to Build Safety Within Your Team
Why This Requires Leadership-Identity: Building safety involves creating an environment of trust and openness. Leaders set the tone for psychological safety in their teams.
- Challenges of Operating from Self-Identity: Personal insecurities can hinder the creation of a safe environment, leading to team reluctance to share.
- Challenges of Operating from Role Identity: Focusing solely on tasks can neglect the emotional well-being of team members, reducing overall safety.
Lesson #9: How to Speak So People Will Listen
Why This Requires Leadership-Identity: Effective communication from a leader commands attention and respect. Leaders need to inspire and motivate their team through clear and compelling speech.
- Challenges of Operating from Self-Identity: Personal communication styles may not resonate with everyone, leading to misunderstandings and disengagement.
- Challenges of Operating from Role Identity: Role-specific jargon can confuse or alienate team members, reducing the impact of the message.
Lesson #12: How to Listen So People Will Speak
Why This Requires Leadership-Identity: Active listening fosters an open dialogue and trust. Leaders must show genuine interest in their team's ideas and concerns.
- Challenges of Operating from Self-Identity: Personal biases may affect listening, leading to selective hearing and missed valuable insights.
- Challenges of Operating from Role Identity: Focusing on role-related issues may limit understanding, preventing a full grasp of team concerns and ideas.
Support: each lesson will include all the relevant facts and information you need to grow your Knowledge, how to apply the core traits of each Cognitive Colour to convert that Knowledge into Skill, as well as a number of practice scenarios you may use to enhance your Abilities by applying your new Skills across multiple situations.
Often the most impactful learning comes from direct, one-on-one sessions tailored to your questions. Here again is the link to book those with your designated CultureSmith representative.



